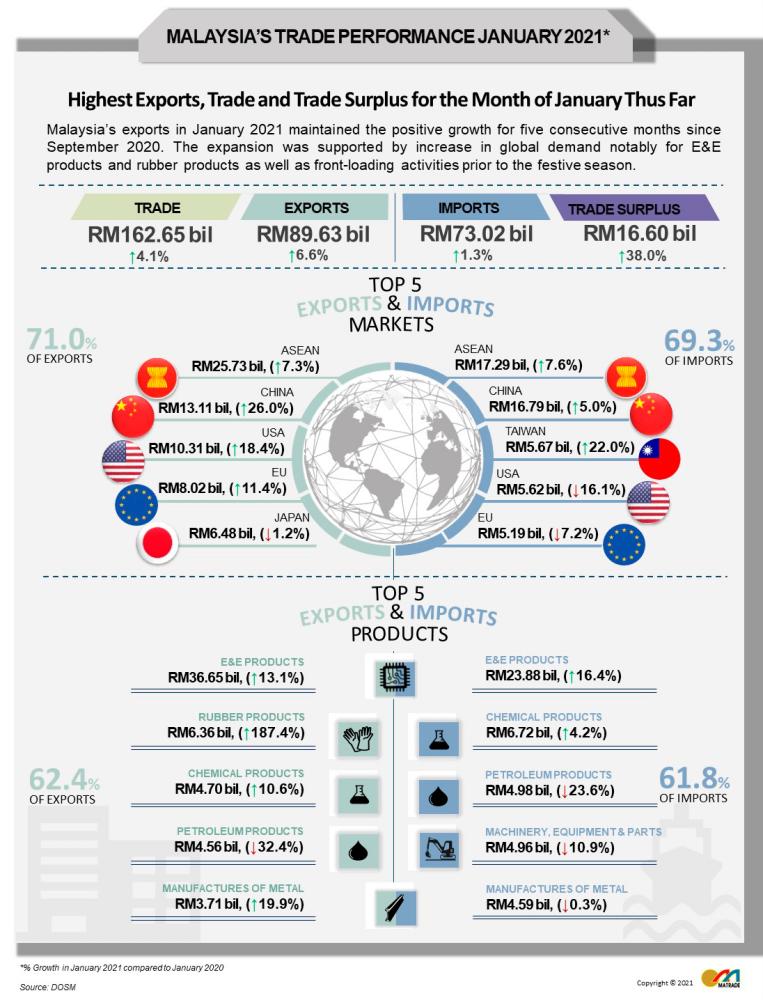
PETALING JAYA: Malaysia’s export rose 6.6% year-on-year (yoy) to RM89.63 billion in January 2021, the highest for the month of January thus far, while this also marks the fifth consecutive month of positive growth, according to Malaysia External Trade Development Corp (Matrade).
It noted that the expansion was supported by increase in global demand notably for electrical and electronic (E&E) and rubber products as well as front-loading activities prior to the festive season.
Higher exports were seen to China, the US, Vietnam, Singapore and Hong Kong.
Meanwhile, the agency stated that imports for the month grew 1.3% yoy to RM73.02.
On the whole, total trade rose 4.1% to RM162.65 billion, the highest value registered for the month of January. Consequently, Malaysia’s trade surplus surged by 38% to RM16.6 billion, sustaining a double-digit growth for eight consecutive months.
Compared to the preceding month, total trade, exports, imports and trade surplus decreased by 4.8%, 6.4%, 2.7% and 19.8%, respectively.
The agency highlighted that the export of manufactured goods contributed to 88.5% of total exports, translating to an 11.7% yoy growth to RM79.36 billion, supported by higher export of E&E products notably in automotive industry, 5G network and smart devices.
On the other hand, the exports of rubber products, especially rubber gloves which showed resilient performance, registering triple-digit growth for five consecutive months.
It also reported an increased export for the manufactures of metal, chemicals and chemical products as well as optical and scientific equipment.
Exports of agricultural goods fell 7.2% yoy to RM5 billion due to lower exports of palm oil and palm oil based agriculture products and mining goods exports shrank 31% to RM4.93 billion on lower exports of liquefied natural gas (LNG) and crude petroleum
Among the major exports for the month are, e&e products valued at RM36.6 billion (40.9% of total exports, +13.1% yoy), rubber products valued at RM6.36 billion (7.1% of total exports, +187.4% yoy), chemicals and chemical products valued at RM4.7 billion (5.2% of total exports, +10.6% yoy), petroleum products valued at RM4.56 billion (5.1% of total exports, -32.4% yoy) and manufactures of meta valued at RM3.71 billion (4.1% of total exports, +19.9% yoy).
On a month-on-month (mom) basis, Martrade listed that exports of manufactured, agriculture and mining goods declined by 3.2%, 40.2% and 1.8%, respectively.
For the month, Malaysia trade with Asean constituted 26.5% of its total trade, which translated to a 7.4% growth yoy to RM43.03 billion as exports grew for two straight months. January saw a 7.3% growth yoy to RM25.73 billion buoyed by higher exports of E&E products, while imports from Asean picked up by 7.6% to RM17.29 billion.
Meanwhile, the agency said that Malaysia’s export to China recorded double-digit growth for three straight months.
In January, trade with China jumped 13.3% yoy to to RM29.9 billion, accounting for 18.4% of Malaysia’s total trade. Exports to China has seen double digit growth since November 2020, expanding by 26% to RM13.11 billion in January 2021.
The increase is attributed to higher exports of e&e products, iron and steel products as well as other manufactures especially solid-state storage devices (SSD), while imports from China expanded by 5% to RM16.79 billion.
On the other hand, the country’s total imports grew 1.3% yoy to RM73.02 billion in January 2021 with the three main categories of imports by end use accounted for 72.8% of the total.
Matrade listed that the import of intermediate goods stood at RM39.39 billion or 53.9% of total imports rose 1.4% yoy, following higher imports of processed industrial supplies, capital goods valued at RM7.24 billion or 9.9% of total imports had declined 5.4% yoy, due mainly to reduced imports of capital goods and consumption goods, valued at RM6.54 billion or 9% of total imports, rose 1.3% yoy, as a result of higher imports of primary food and beverages mainly for household consumption, especially coffee, tea and spices.